How to Measure the Motion Quality of Each Axis in Stocker?
Case | How to Measure the Motion Quality of Each Axis in Stocker?The Stocker automated handling system autonomously performs material transportation tasks. How can we ensure the efficient operation of each axis in the system?
Stocker Automated Handling System
The Stocker automated handling system is an intelligent storage and transportation solution that autonomously transfers goods from one location to another, reducing manual operations. One of its key design objectives is to maximize space utilization, enabling more efficient use of warehouse or production line space. The system can autonomously navigate within warehouses or factories, avoiding obstacles and executing tasks along pre-defined routes. It helps improve production efficiency, reduce costs, enhance safety, and make warehouse or production line management more intelligent and automated.

The Stocker Automated Handling System typically uses a multi-axis motion control system.
If any of these axes experience abnormalities, various issues may arise. For example, an X-axis malfunction may impact horizontal movement,
causing misalignment or preventing the transporter from reaching the correct target position. A Y-axis malfunction may affect vertical movement,
leading to inaccuracies in lifting or lowering the transporter, potentially misplacing materials.
These axis abnormalities can result in inaccurate movements, incorrect positioning, unstable elevation, and even safety risks.
So, how can we monitor Stocker to ensure the system operates efficiently?
Monitoring Explanation
VMS-ML Machine Learning Intelligent Monitoring System
The VMS-ML system learns the correct movement behaviors as a benchmark to monitor and diagnose individual movements.
By analyzing system data, it detects abnormalities or instabilities in specific actions, allowing for predictive maintenance
and preventing unexpected failures.
Measurement Status
1. X-Axis Foup Pickup Action Recognition (Horizontal vs. Vertical Comparison)
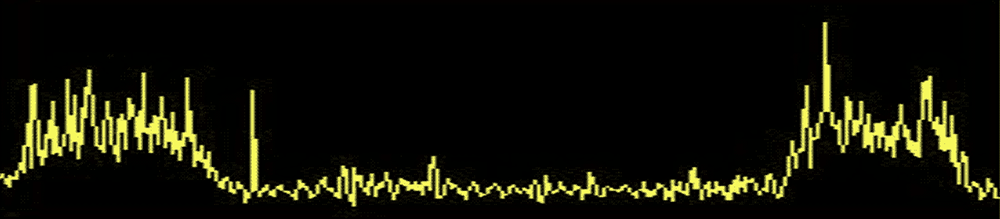
1. X-Axis Foup Pickup Action Recognition (Horizontal vs. Vertical Comparison)

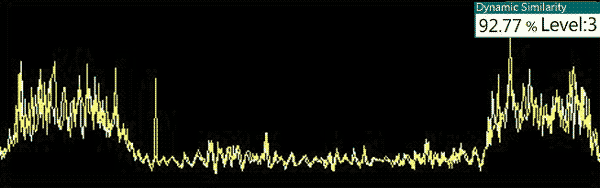
Result: PASS (92.77%)
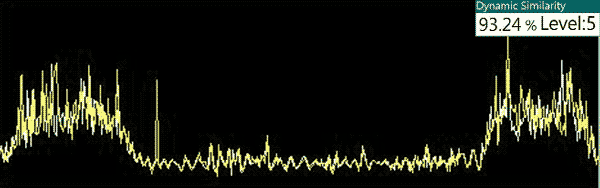
Result: PASS (93.24%)
Action: Crane extends forward (X-axis), lifts foup (Z-axis), then retracts to the original position (X-axis) and stops.

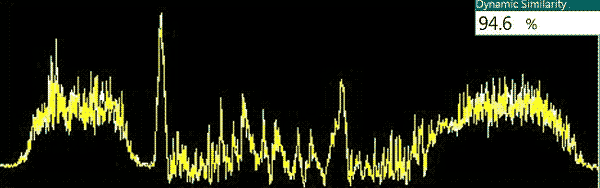
Result: PASS (94.6%)
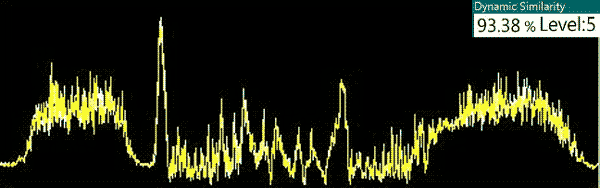
Result: PASS (93.38%)
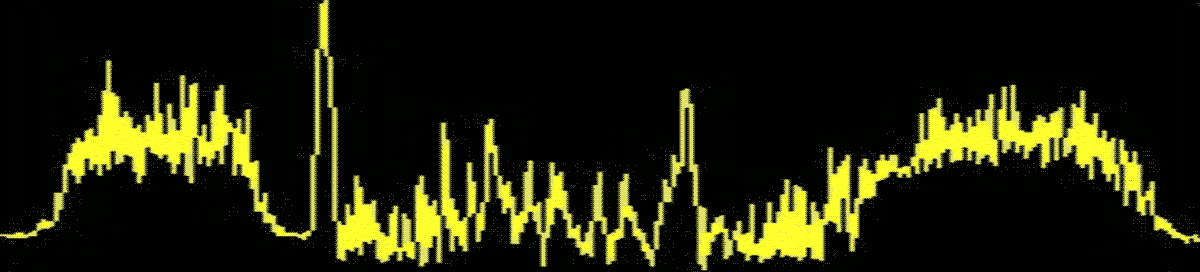
2. Machine Learning Anomaly Simulation Test (Process Anomaly Visualization Management)
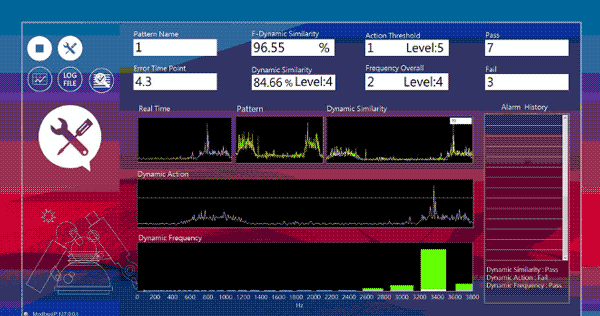
X-Axis Retraction Stop Anomaly
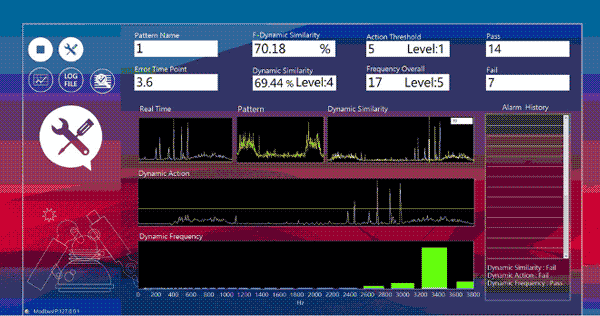
Severe X-Axis Wear
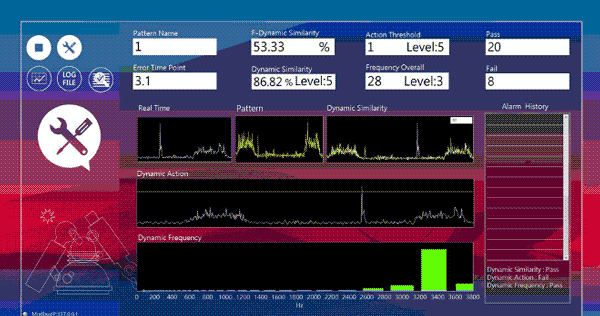
Surge Anomaly
Measurement Conclusion
Using the VMS-ML Machine Learning Intelligent Monitoring System, the correct movement behaviors are learned and used as a benchmark to monitor and diagnose each axis movement. The system identifies anomalies or unstable conditions in Stocker’s operations, enabling predictive maintenance at the right time. This ensures the proper functioning of the Stocker automated handling system, facilitates fault detection, and allows for rapid repairs, helping maintain overall system efficiency.
VMS-ML Machine Learning Intelligent Monitoring System


