The First Step to Implementing ESG
Technology Concept | The First Step to Implementing ESGESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It is a framework that incorporates environmental, social, and corporate governance factors into business considerations.
An Essential Part of Business Operations? Reasons for Implementation
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), a framework that integrates these three key aspects into business strategy. The **Environmental** aspect includes a company’s impact on the environment, such as reducing pollution and lowering carbon footprints. The **Social** aspect involves a company’s interactions with employees, customers, suppliers, and corporate social responsibility (CSR), including community investments, support for education, and public welfare initiatives. The **Governance** aspect focuses on corporate management transparency, accountability, and risk management.
How to Implement
1. Small Actions Can Make a Big Environmental Impact
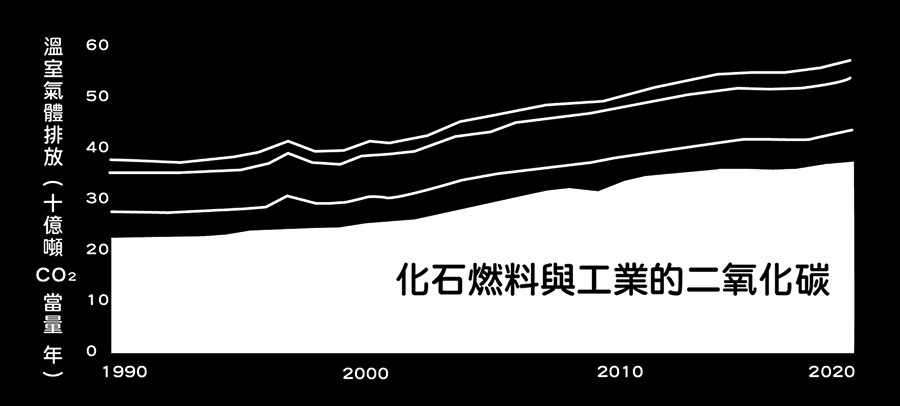
In 2024, the world experienced record-breaking high temperatures, with some regions exceeding 50°C. The planet is facing severe ecosystem degradation, threatening many species. Human activities, particularly industrial operations, have significantly contributed to greenhouse gas emissions, accelerating global warming. Therefore, optimizing energy use is the first step toward ESG implementation.
Optimizing Energy Usage
With rising energy costs and increasing environmental pressures, industrial enterprises must adopt proactive energy-saving measures to maintain competitiveness and sustainability. EMS can help businesses develop optimization strategies to enhance overall energy efficiency.
EMS Smart Energy Management System
One of the core functions of the EMS Smart Energy Management System is intelligent energy monitoring. By utilizing sensors installed on equipment and facilities, EMS collects and analyzes real-time energy usage data, providing a comprehensive view of power consumption. These insights enable managers to identify sources of energy waste and implement targeted energy-saving measures.
EMS Smart Energy Management SystemECOWATCH Smart Energy Management
ECOWATCH Smart Energy Management System complies with the ISO50001 energy management standard and meets government energy-saving and carbon reduction regulations. By leveraging data analytics and AI-powered predictions, it provides users with deeper insights and better decision-making support.
ECOWATCH Smart Energy Management
How to Implement
2. Enhance Equipment Efficiency & Reduce Carbon Emissions
Improving equipment efficiency is crucial for reducing costs and lowering carbon emissions. By monitoring equipment status, efficiency can be maximized while avoiding unnecessary power consumption. Establishing regular maintenance plans ensures that equipment operates in optimal conditions. Monitoring systems can track and predict potential failures, enable predictive maintenance, and extend equipment lifespan.
Residual Life Prediction
When equipment is used normally and operates under stable conditions, its lifespan becomes a key factor in production efficiency. By applying different monitoring techniques based on equipment characteristics, users can determine how much longer the equipment can function, when maintenance should be scheduled after an alert, and the optimal maintenance order for machines.
Rotary Motor Equipment
Factories are filled with automated equipment, most of which involve motor rotors. Monitoring the rotor condition is key to ensuring normal machine operations. By measuring vibration signals, essential insights into machine conditions can be obtained.
Rotary Motor EquipmentCyclic Production Equipment
This category includes machines with multiple mechanisms and motors that execute repetitive cyclic production tasks. Examples include robotic arms, CNC machine tools, stamping and forging machines.
Cyclic Production Equipment
How to Implement
3. Adopting Green Energy
Taiwan's green energy sector primarily focuses on solar power, wind power, and hydropower. Recently, solar energy has gained significant popularity, with the government introducing a two-year solar energy promotion plan to encourage small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and private organizations to adopt solar panels. This also helps reduce reliance on a single energy source, minimizing price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
Integration of Solar Power and Energy Management Systems
In response to global warming and the energy crisis, achieving sustainability has become a common goal for nations. The integration of solar power and energy management systems provides an effective solution to support this objective.
Solar Self-Generation Plan
Factories are filled with automated equipment, most of which contain motor rotors. Monitoring the rotor condition is key to ensuring normal machine operations. By measuring vibration signals from machines, valuable operational insights can be obtained.
Solar Self-Generation PlanAquavoltaics Application Case
Kouhu Taiwan Tilapia Technology
Kouhu Taiwan Tilapia Technology has installed large-scale solar panels and management systems, integrating the EMS system to achieve dynamic energy allocation. The EMS system optimizes solar energy usage based on power demand, increasing the self-sufficiency rate of aquaculture to over 80%, setting an example for sustainable energy utilization.
Support
Other ESG-Related Topics